本文讲述使用JSP实现用户登录,包括用户登录、注册和退出功能等。
1.系统用例图

2.页面流程图

3.数据库设计
本例使用oracle数据库
创建用户表
包括id,username,password和email,共4个字段
create table P_USER
(
id VARCHAR2(50) not null,
username VARCHAR2(20),
password VARCHAR2(20),
email VARCHAR2(50)
)
tablespace USERS
pctfree 10
initrans 1
maxtrans 255
storage
(
initial 64
minextents 1
maxextents unlimited
);
— Add comments to the table
comment on table P_USER
is ‘用户表’;
— Add comments to the columns
comment on column P_USER.id
is ‘id’;
comment on column P_USER.username
is ‘用户名’;
comment on column P_USER.password
is ‘密码’;
comment on column P_USER.email
is ’email’;
4.页面设计
4.1登录页面
login.jsp
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”>
<html>
<head>
<base href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/<%=basePath%>”>
<title>登录页面</title>
<meta http-equiv=”pragma” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”cache-control” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”expires” content=”0″>
<meta http-equiv=”keywords” content=”keyword1,keyword2,keyword3″>
<meta http-equiv=”description” content=”This is my page”>
<!–
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/styles.css”>
–>
</head>
<body>
<form action=”login_action.jsp” method=”post”>
<table>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″>登录窗口</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”username” />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”password” />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″><input type=”submit” value=”登录” /> <a href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/register.jsp”>注册</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
页面效果

4.2登录逻辑处理页面
login_action.jsp
<%@ page import=”java.sql.*” %>
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<%
String username=request.getParameter(“username”);
String password=request.getParameter(“password”);
if(username==null||””.equals(username.trim())||password==null||””.equals(password.trim())){
//out.write(“用户名或密码不能为空!”);
System.out.println(“用户名或密码不能为空!”);
response.sendRedirect(“login.jsp”);
return;
//request.getRequestDispatcher(“login.jsp”).forward(request, response);
}
boolean isValid=false;
Connection con=null;// 创建一个数据库连接
PreparedStatement pre=null;// 创建预编译语句对象,一般都是用这个而不用Statement
ResultSet result=null;// 创建一个结果集对象
try
{
Class.forName(“oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver”);// 加载Oracle驱动程序
//System.out.println(“开始尝试连接数据库!”);
String url=”jdbc:oracle:” + “thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl”;// 127.0.0.1是本机地址,orcl是Oracle的默认数据库名
String user=”scott”;// 用户名,系统默认的账户名
String pwd=”tiger”;// 你安装时选设置的密码
con=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);// 获取连接
// System.out.println(“连接成功!”);
String sql=”select * from p_user where username=? and password=?”;// 预编译语句,“?”代表参数
pre=con.prepareStatement(sql);// 实例化预编译语句
pre.setString(1, username);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
pre.setString(2, password);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
result=pre.executeQuery();// 执行查询,注意括号中不需要再加参数
if (result.next()){
isValid=true;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try
{
// 逐一将上面的几个对象关闭,因为不关闭的话会影响性能、并且占用资源
// 注意关闭的顺序,最后使用的最先关闭
if (result !=null)
result.close();
if (pre !=null)
pre.close();
if (con !=null)
con.close();
//System.out.println(“数据库连接已关闭!”);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(isValid){
System.out.println(“登录成功!”);
session.setAttribute(“username”, username);
response.sendRedirect(“welcome.jsp”);
return;
}else{
System.out.println(“登录失败!”);
response.sendRedirect(“login.jsp”);
return;
}
%>
使用JDBC连接数据库,如果用户名或密码为空时,还是跳转到登录页面login.jsp
如果用户名和密码不为空,进行连接数据库查询用户表,如果能够查询到记录,表示登录成功,将用户信息保存到session,跳转到欢迎页面welcome.jsp
如果根据用户名和密码查询不到记录,表示登录失败,重新跳转到登录页面login.jsp
4.3欢迎页面
welcome.jsp
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”>
<html>
<head>
<base href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/<%=basePath%>”>
<title>My JSP ‘welcom.jsp’ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv=”pragma” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”cache-control” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”expires” content=”0″>
<meta http-equiv=”keywords” content=”keyword1,keyword2,keyword3″>
<meta http-equiv=”description” content=”This is my page”>
<!–
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/styles.css”>
–>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td><img src=”https://www.jb51.net/article/images/logo4.png” />
</td>
<td><img src=”https://www.jb51.net/article/images/logo2.png” height=”90″ />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″><hr />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<table>
<tr>
<td><a>Main</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu1</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu2</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu3</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu4</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu5</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu6</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu7</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a>Menu8</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table></td>
<td>
<form action=”loginout.jsp” method=”post”>
<table>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″>登录成功!</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>欢迎你,</td>
<td>${username }</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″><input type=”submit” value=”退出” /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
使用EL表达式展示用户信息
效果

4.4欢迎页退出逻辑处理页面
loginout.jsp
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”>
<html>
<head>
<base href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/<%=basePath%>”>
<title>My JSP ‘loginout.jsp’ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv=”pragma” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”cache-control” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”expires” content=”0″>
<meta http-equiv=”keywords” content=”keyword1,keyword2,keyword3″>
<meta http-equiv=”description” content=”This is my page”>
<!–
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/styles.css”>
–>
</head>
<body>
<%
session.removeAttribute(“username”);
response.sendRedirect(“login.jsp”);
%>
</body>
</html>
将session的用户信息移除,跳转到登录页面login.jsp
4.5注册页面
register.jsp
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN”>
<html>
<head>
<base href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/<%=basePath%>”>
<title>注册页面</title>
<meta http-equiv=”pragma” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”cache-control” content=”no-cache”>
<meta http-equiv=”expires” content=”0″>
<meta http-equiv=”keywords” content=”keyword1,keyword2,keyword3″>
<meta http-equiv=”description” content=”This is my page”>
<!–
<link rel=”stylesheet” type=”text/css” href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/styles.css”>
–>
</head>
<body>
<form action=”register_action.jsp” method=”post”>
<table>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″>注册窗口</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”username” /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”password1″ /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>确认密码:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”password2″ /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>email:</td>
<td><input type=”text” name=”email” /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″><input type=”submit” value=”注册” /> <a href=”https://www.jb51.net/article/login.jsp”>返回</a></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
当在登录页面点击“注册“时打开用户注册页面
效果
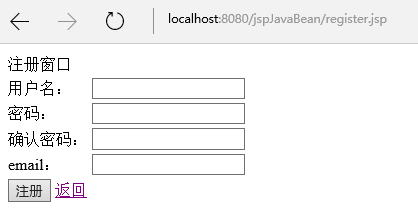
4.6注册逻辑处理页面
register_action.jsp
<%@ page import=”java.sql.*” %>
<%
String path=request.getContextPath();
String basePath=request.getScheme()+”://”+request.getServerName()+”:”+request.getServerPort()+path+”/”;
%>
<%
String username=request.getParameter(“username”);
String password1=request.getParameter(“password1”);
String password2=request.getParameter(“password2”);
String email=request.getParameter(“email”);
if(username==null||””.equals(username.trim())||password1==null||””.equals(password1.trim())||password2==null||””.equals(password2.trim())||!password1.equals(password2)){
//out.write(“用户名或密码不能为空!”);
System.out.println(“用户名或密码不能为空!”);
response.sendRedirect(“register.jsp”);
return;
//request.getRequestDispatcher(“login.jsp”).forward(request, response);
}
boolean isValid=false;
Connection con=null;// 创建一个数据库连接
PreparedStatement pre=null;// 创建预编译语句对象,一般都是用这个而不用Statement
ResultSet result=null;// 创建一个结果集对象
try
{
Class.forName(“oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver”);// 加载Oracle驱动程序
//System.out.println(“开始尝试连接数据库!”);
String url=”jdbc:oracle:” + “thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:orcl”;// 127.0.0.1是本机地址,orcl是Oracle的默认数据库名
String user=”scott”;// 用户名,系统默认的账户名
String pwd=”tiger”;// 你安装时选设置的密码
con=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);// 获取连接
//System.out.println(“连接成功!”);
String sql=”select * from p_user where username=?”;// 预编译语句,“?”代表参数
pre=con.prepareStatement(sql);// 实例化预编译语句
pre.setString(1, username);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
result=pre.executeQuery();// 执行查询,注意括号中不需要再加参数
if (!result.next()){
sql=”insert into p_user(id,username,password,email) values(?,?,?,?)”;// 预编译语句,“?”代表参数
pre=con.prepareStatement(sql);// 实例化预编译语句
pre.setString(1, System.currentTimeMillis()+””);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
pre.setString(2, username);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
pre.setString(3, password1);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
pre.setString(4, email);// 设置参数,前面的1表示参数的索引,而不是表中列名的索引
pre.executeUpdate();// 执行
isValid=true;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try
{
// 逐一将上面的几个对象关闭,因为不关闭的话会影响性能、并且占用资源
// 注意关闭的顺序,最后使用的最先关闭
if (result !=null)
result.close();
if (pre !=null)
pre.close();
if (con !=null)
con.close();
//System.out.println(“数据库连接已关闭!”);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(isValid){
System.out.println(“注册成功,请登录!”);
response.sendRedirect(“login.jsp”);
return;
}else{
System.out.println(“用户名已存在!”);
response.sendRedirect(“register.jsp”);
return;
}
%>
首先判断用户名和密码是否为空,以及密码和确认密码是否一致,如果上述条件不成立时,返回到注册页面register.jsp
如果上述条件成立,就根据用户名到数据库查询,如果能够查询到记录,说明用户名已经存在,返回到注册页面register.jsp
如果查询不到记录,说明此用户名可用来进行注册,使用JDBC向用户表 插入1条记录;之后跳转到登录页面login.jsp
5.总结
本例使用JSP实现用户登录,编写过程中,主要遇到了2个小问题。
5.1查询之后,判断记录是否存在,需要使用 if (!result.next()),而不是通常查询中使用的while循环,这一点需要注意,特别是在处理注册时。
5.2关于JSP页面的编译报错问题。
当在JSP小脚本中中使用return时要慎重,很可能会出现编译错误。
处理方法是,JSP主页面只使用JSP小脚本,保证return之后没有还需要编译的内容即可。
以上即为使用JSP实现用户登录的简单介绍,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。



